Soon it will be time: On the Knowledge Hub Hamburg you can find free knowledge and share your knowledge yourself. The content comes from Hamburg Labs, Makerspaces, partners and dedicated volunteers from Hamburg. Here we write down what's new and link to what's known, because everything starts with education!
Open education for all!
Where do I share my knowledge? Soon: Here! The Knowledge Hub Hamburg is all about open knowledge, also called OER (Open Educational Resources). OER can be many things: an article, a wiki, a video or a presentation, together or individually. The only decisive factor is that a Creative Commons license is attached to the media. By doing so, the creator decides that it is open knowledge. Of course, you’ll learn how to do that here soon.
Open knowledge makes everything much easier!
By making sharing desirable, a large annoying part of legal issues, access restrictions, and more simply falls away. Open working is one of Fab City’s core cultures.
Why a Knowledge Hub?
The ideas of Fab Labs and self-sustaining Fab Cities are all based on education and knowledge. A culture of learning is the foundation.
Everything starts with know-how!
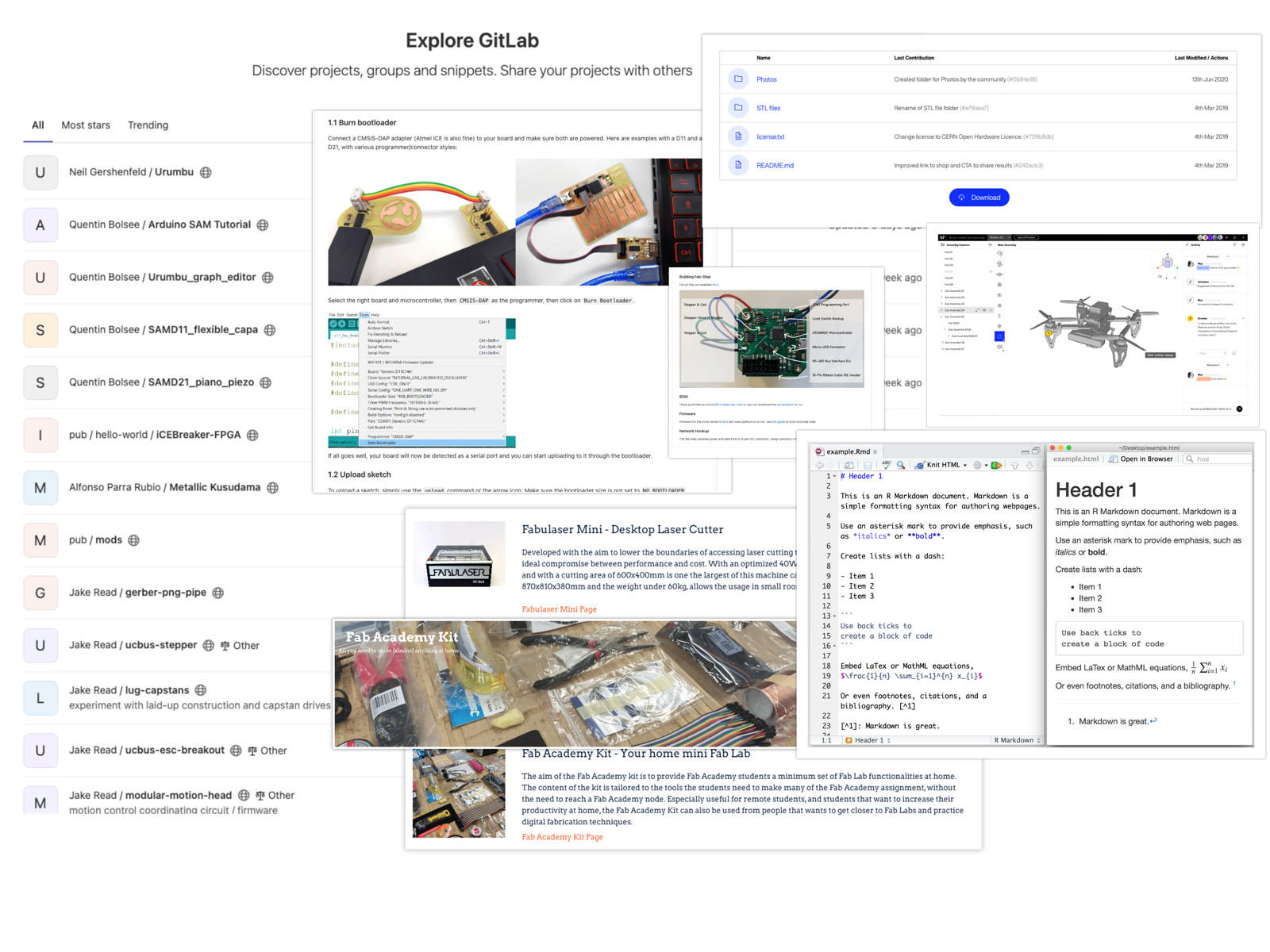
The goal of the Knowledge Hub is to make global effective collaboration on knowledge on open Git technology easy to use to simplify knowledge creation and sharing.

How will we learn in 2022?
Studies among Fab Labs show that Youtube is the most popular platform for learning.
Also very common are Git repositories, which bring the principles of distributed open source software development to the hardware space.
Sharing build instructions in Markdown format has become a global standard because it works everywhere and requires no extra software. The Knowledge Hub also relies on Git and Markdown as a basis.
Hamburg know-how!
Hamburg is one of the largest Fab Cities in the world. Through the local network, Hamburg has a broad knowledge. The many practical knowledge of the Hamburg Makerspaces is of course not to be sneezed at. With research institutions and the Helmut Schmidt University, a research focus is also part of the network. Especially through the INTERFACER project, there is extensive digital expertise. The Fab City project develops open fab lab machines. Together with the Build Workshops, competencies in workshop design and open source hardware documentation are being built. Together with Bucerius Law School, extensive knowledge of IP law (intellectual property) is available. With the Open Toolchain Foundation there are many experts in the field of Open Source Software.
The concept of the Hamburg Knowledge Hub
1. code: Technologically open, reliable and compatible.
2. UX/UI: Make sharing knowledge simple and reduced.
3. Content: Curation and community involvement.
1. code
At its core, knowledge in the form of open educational resources (OER) means sorting information.
We collect information and make it available in a structured way. The Internet already offers endless possibilities for this, but often in the form of free learning platforms.
An expensive learning system that quickly becomes outdated is not the solution either.
Therefore, we rely on the best known and most universal standard among makers: Markdown. Markdown is simple and quick to learn. And there are numerous text editors that support Markdown out of the box. In the end, we’ll use it to create technically robust websites, just like we’re all hopefully used to.
How to create and edit content?
For this, we simply make use of well-known Git platforms (in our case, Gitlab). These come with numerous editing and collaboration features. So others take care of that. The thing we want to be good at is embedding the content of Git servers with us attractively and clearly in the Knowledge Hub.
Since they are public sources, this allows all sites with a Knowledge Hub to curate the same public sources in their own way.
Using Git’s collaboration features, all sources can also be edited globally collaboratively at any time.
2. UX/UI
Most learning platforms are boring and complicated.
Wikipedia, as a positive example, is so attractive because it is so simple and low-threshold. Put simply, there is a search, pages, and links.
The goal of the Knowledge Hub is also to be a very simple and minimalistic knowledge platform. We use the standard layout of a wiki and Markdown.
Because of the simplicity, the technology moves into the background and does not get outdated so quickly.
3. content
Our culture at Fab City thrives on events, community, inventiveness, making and exciting projects. Wherever encounters occur, new knowledge is also created. This is where it comes down to each individual to make the effort to share their knowledge with others every now and then.
It is this culture that makes the difference!
Through the INTERFACER project, we were able to obtain the initial funds to launch the Knowledge Hub. If you care about knowledge management and education, you should definitely get active and make our Knowledge Hub even better. The Fab City Hamburg team will continuously strive to promote our knowledge sharing culture in creative ways.
FAQ
What is OER
OER stands for Open Educational Resource, meaning (one or more) media that contain free knowledge, i.e. have a CC license. In the Knowledge Hub, this is a page with any number of subpages. You can use text, images, video and more to share your knowledge just like in a classic online article.
What is the difference between a Knowledge Hub post and other websites?
A Knowledge Hub post is technically similar to a blog article, except with additional metadata. The metadata makes the knowledge more structured and sustainable to use.
What does the Fab City Full Stack have to do with this?
We use the Full Stack as a content orientation to categorize knowledge contributions.
Knowledge consists of ordered information. In the case of Fab City Hamburg Knowledge Hub, we want to categorize the information based on the underlying concepts of a FabCity. I.e. we orient ourselves to the seven levels of the Fab City Full Stack (which serve to implement the Fab City Vision) in order to be able to search or filter by them.
What is the metadata?
The metadata for each knowledge article is as follows:
-
Author: Author Name Last Name
-
Category: Learning
-
Language: English
-
License: CC-BY-SA 4.0
-
SDG: 12
-
Type: Tutorial, Instruction
-
Hashtag: keyword1, keyword2
Explanations.
The author is important for users to build a reputation.
Category This is from the Full Stack. There are the following seven:
- Physical Infrastructure
- Digital infrastructure
- Learning
- Network
- Strategies
- Metrics
- Incubation
SDG stands for Sustainable Development Goals (Sustainable Development Goals). We probably often use SDG 12 (ensure sustainable consumption and production patterns).
Type is a free tag cloud. Use whatever you think will be most helpful. Use it like a hashtag.
The rest should be obvious :)
What can I write?
Fab City Hamburg stands for a set of values and a strong vision for 2054, so in that sense you can post anything where you think it will help us. We just make sure that nothing illegal is posted, for example.
Learn from good contributions and good wikis. You’ll also find instructions on the Knowledge Hub on how to successfully write up open knowledge (including detailed instructions on license and metadata).
What's the difference between open source hardware documentation and open knowledge (OKR)?
In INTERFACER we are building a distributed database for product or project documentation documentation (known as FCOS Core). The knowledge that is published here always has a clear relation to the respective project.
An OKR page in the Knowledge Hub, on the other hand, usually lacks this direct reference and is more general knowledge. Topics like “How do I recycle plastic?”, material knowledge, knowledge about liability and copyright, etc. are meant for example.
The Knowledge Hub is therefore there to make additional knowledge about projects available centrally. So ideally, documentation links to knowledge from the Knowledge Hub.
Is the Knowledge Hub a Wiki?
Yes. A very large one.
However, it is a minimalist open wiki developed by Fab City Hamburg itself.
The main reason for this decision is that we want to be independent and free to design our Knowledge Hub and make it available to other Fab Cities for free. All open source wikis were far too extensive and complicated to be included. Since there are already many wikis with markdown based database, we focus mainly on frontend design and maximum ease of use.
Do I need a login?
No. Anyone can just get started. It is very important to us that contributing is as easy as possible. However, your contribution will not end up on the Knowledge Hub right away, but will first be reviewed and approved by a Fab City person.
We may well introduce another login in the future to offer even more comprehensive features.
What can I upload to the Knowledge Hub?
Pages
A page is content created directly on fabcity.hamburg. For this you have all the editing options that a modern text editor offers you (images, lists, accordion, subpages, TOC, …). This content creates a page (technically: a public Markdown file in our repository).
Link to a website (external).
We also want to curate resources that already exist. We link to a URL and add a small description and some information (metadata), and we’re done.
We reproduce a source (embed an external public .md source).
Let’s say we found a great wiki that we like a lot and that is also based on individual .md pages. With no (or only minor) changes, we can just take the raw source and output it to our website so that it has the same design as our internal pages.
How can I edit posts
We use Gitlab as our platform for editing contributions. If your post is approved, you can suggest a change via Gitlab and it will be reviewed and approved. Each page has a small “edit” button.
Together smarter
You like Knowledge Hub and want to contact the team?